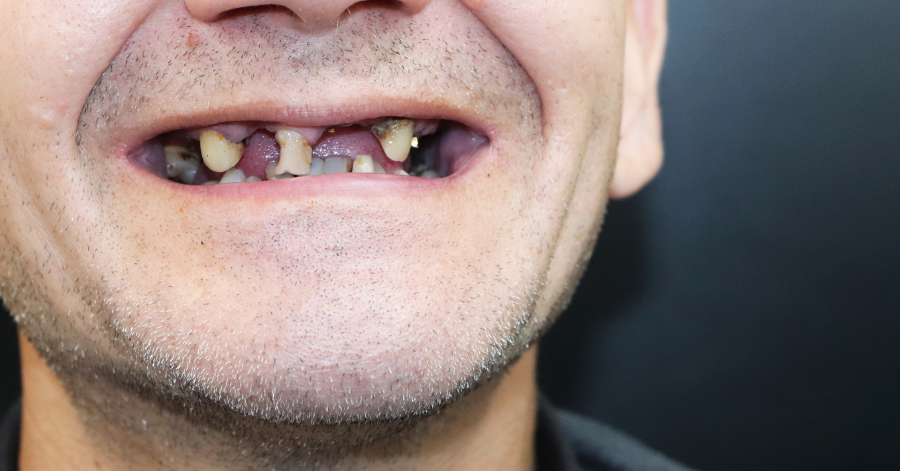
Oral Health Conditions Linked to Heart Disease
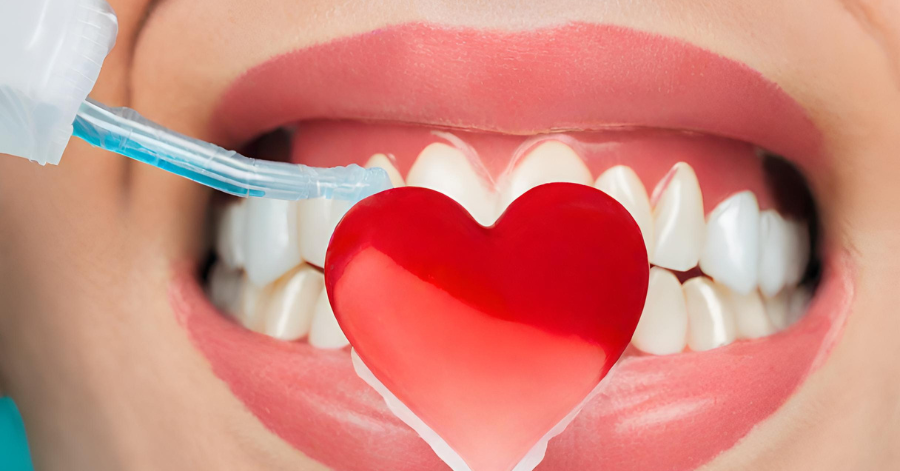
Good oral health goes beyond having a beautiful smile. It is also closely connected to our overall well-being, particularly our cardiovascular health. Research has revealed a significant link between oral health conditions and heart disease, highlighting the importance of taking care of our teeth and gums for the sake of our hearts.
Studies have shown that poor oral health can contribute to the development of heart disease. Bacteria from gum infections and dental plaque can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation and putting strain on the cardiovascular system. This raises the risk of conditions such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
Understanding the connection between oral health and heart disease is essential for individuals and healthcare providers alike. By prioritizing good dental care and maintaining proper oral hygiene, we can help protect our heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Key Takeaways:
- Poor oral health is linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
- Oral bacteria and inflammation can contribute to cardiovascular problems.
- Gum disease and dental plaque can lead to atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
- Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene are crucial for heart disease prevention.
- Collaboration between dentists and cardiologists can lead to better outcomes for patients.
Understanding the Oral Health and Heart Disease Connection
When it comes to taking care of our bodies, we often overlook the impact that dental health can have on our overall well-being. However, research has increasingly shown a significant connection between oral health and heart disease. Understanding this link is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart.
One of the key factors in the oral health and heart disease connection is the presence of oral bacteria in the bloodstream. When there is an infection or inflammation in the mouth due to poor oral hygiene or gum disease, the bacteria can enter the bloodstream and travel to the heart. This can lead to the formation of blood clots, narrowing of the arteries, and an increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
Dental care plays a vital role in preventing heart disease. By maintaining good oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, we can reduce the presence of harmful bacteria in the mouth. This, in turn, lowers the chances of these bacteria reaching the heart and causing cardiovascular issues.
| Impact of Dental Health on Heart Health |
|---|
| Oral bacteria can enter the bloodstream and contribute to cardiovascular problems |
| Good dental care, such as regular brushing and flossing, can prevent heart disease |
Gum Disease and Heart Health
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is not only a threat to your oral health but also poses risks to your cardiovascular system. Research has shown a strong association between gum disease and heart problems, highlighting the importance of maintaining healthy gums for overall heart health.
Periodontal disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gums and the bone supporting the teeth. When left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and contribute to the development of various health issues, including heart disease.
The link between gum disease and heart health lies in the bacteria and inflammation associated with periodontal disease. The bacteria responsible for gum disease can enter the bloodstream through the infected gums, causing inflammation in blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the heart.
This chronic inflammatory response can contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and potentially leading to cardiovascular problems, such as heart attacks or strokes.
To further understand the connection between gum disease and heart health, researchers have investigated the role of specific bacteria commonly found in periodontal disease. One study found that certain oral bacteria, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, can directly contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
“The link between gum disease and heart health lies in the bacteria and inflammation associated with periodontal disease.”
Moreover, the inflammation caused by gum disease can also increase systemic inflammation throughout the body, which is known to be a risk factor for heart disease.
To mitigate the cardiovascular risks associated with gum disease, it is crucial to prioritize oral health and maintain good gum hygiene. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can help identify and treat gum disease in its early stages, preventing further complications.
In addition to professional dental care, practicing good oral hygiene at home is essential. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. These simple yet effective habits can help keep your gums healthy and reduce the risk of gum disease-related cardiovascular problems.
By understanding the connection between gum disease and heart health and taking proactive steps to maintain good gum hygiene, you can protect not only your smile but also your overall cardiovascular well-being.
Oral Hygiene and Heart Disease
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for preserving heart health. Dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that accumulates on the teeth, can have a significant impact on the cardiovascular system. When left untreated, dental plaque can lead to inflammation and infection, which increases the risk of heart disease.
Research has shown that the bacteria found in dental plaque can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque buildup can restrict blood flow to the heart, potentially leading to heart attacks or strokes.
Fortunately, practicing proper oral hygiene can help reduce the risk of heart disease. Here are some essential tips for maintaining good oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste.
- Use dental floss or an interdental cleaner to clean between your teeth daily.
- Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacterial growth.
- Replace your toothbrush regularly, about every three to four months.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings with your dentist.
By following these oral hygiene practices, you can help remove dental plaque and reduce the risk of heart disease. It’s important to note that good oral hygiene is just one piece of the puzzle. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco use, is also essential for maintaining heart and oral health.
“Practicing good oral hygiene not only helps keep your teeth and gums healthy but also plays a significant role in protecting your heart. By brushing, flossing, and visiting your dentist regularly, you are taking proactive steps towards heart disease prevention.” – Dr. Emily Wilson, Cardiologist
| Oral Hygiene Tips for Heart Health | Description |
|---|---|
| Brush your teeth regularly | Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes using a fluoride toothpaste. This helps remove plaque and bacteria from your teeth. |
| Floss daily | Using dental floss or interdental cleaners, clean between your teeth to remove plaque and food particles that your toothbrush may not reach. |
| Use an antimicrobial mouthwash | Rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash helps reduce bacterial growth and keeps your breath fresh. |
| Replace your toothbrush regularly | To maintain effective cleaning, replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed. |
| Visit your dentist regularly | Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to prevent and detect oral health issues early on. |
Support the well-being of your gums and teeth, fostering a stronger, healthier oral ecosystem
The Relationship Between Oral Health and Heart Conditions
When it comes to maintaining overall health, many people tend to overlook the connection between oral health and heart conditions. However, research has shown a clear link between oral health conditions and an increased risk of heart disease.
One of the key factors contributing to this relationship is the presence of oral bacteria in the bloodstream. When there is gum disease or poor oral hygiene, bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in the blood vessels. This inflammation can then contribute to the development of heart disease.
Furthermore, studies have found that people with gum disease are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular problems such as heart attacks and strokes. The inflammation and infection in the gums can spread to other parts of the body, including the arteries, leading to the formation of plaque and narrowing of the blood vessels.
In addition to oral bacteria, other factors like chronic inflammation and compromised immune function can also play a role in the relationship between oral health and heart conditions. Poor oral health can lead to systemic inflammation, which is associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
To maintain a healthy heart, it is important to prioritize good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice a day, flossing regularly, and scheduling regular dental check-ups. By taking care of your oral health, you can reduce the risk of oral bacteria entering the bloodstream and potentially causing heart problems.
“The connection between oral health and heart conditions highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to healthcare. By taking care of your teeth and gums, you are also taking care of your heart.” – Dr. Emma Smith
Dental Care for Heart Disease Prevention
Proper dental care plays a crucial role in preventing heart disease. By maintaining good oral health, you can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems. Here are some important dental care practices that can help protect your heart:
1. Regular Dental Check-ups
Scheduling regular dental check-ups with your dentist is essential for both your oral health and heart health. During these check-ups, your dentist can detect and treat any potential oral health issues, such as gum disease or infections, that may contribute to heart problems. They can also provide professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar build-up.
2. Proper Brushing and Flossing Techniques
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily are essential for maintaining good oral hygiene. It is important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to thoroughly clean your teeth and gums. Remember to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the backside and along the gumline. Don’t forget to floss between your teeth to remove plaque and food particles that can lead to gum disease.
3. Mouthwash and Antimicrobial Rinse
Using mouthwash and antimicrobial rinse can help kill bacteria in your mouth and maintain a healthy oral environment. These products can help reduce the risk of gum disease and other oral health conditions that may impact heart health. Consult with your dentist to determine the most suitable mouthwash or rinse for your specific needs.
4. Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Good dental care is not the only factor in preventing heart disease. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can also contribute to overall heart health. Avoid smoking or using tobacco products as they not only stain your teeth but also increase the risk of gum disease and heart problems. Additionally, adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Reducing stress levels and maintaining a regular exercise routine further support heart health.
Remember, dental health and heart health are interconnected. By prioritizing your dental care and maintaining good oral hygiene practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and protect your overall cardiovascular health.
Lifestyle Changes for Heart and Oral Health
When it comes to maintaining good heart and oral health, making certain lifestyle changes can have a significant impact. By addressing factors such as smoking, diet, and stress, individuals can improve the health of both their hearts and mouths.
1. Quit Smoking
Smoking is not only harmful to the lungs but also poses a serious threat to heart and oral health. Smoking increases the risk of heart disease by damaging blood vessels and increasing the formation of blood clots. Additionally, smoking can lead to gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancer.
By quitting smoking, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their oral health. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, utilizing nicotine replacement therapy, and adopting healthy coping strategies can help smokers successfully quit.
2. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet not only benefits heart health but also supports good oral health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products provides essential nutrients for both systems. Avoiding excessive consumption of sugary foods and beverages helps prevent tooth decay and gum disease.
Consider incorporating heart-healthy foods such as salmon, walnuts, and olive oil into your diet. These foods are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which promote heart health and help reduce inflammation in the body. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water can also contribute to oral health.
3. Manage Stress
High levels of stress can take a toll on both heart and oral health. Stress can increase blood pressure, trigger heart problems, and lead to habits such as teeth grinding or clenching. These habits can cause dental issues like tooth sensitivity and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies can help manage stress levels. Seeking support from mental health professionals or joining support groups can also provide valuable resources to cope with stress effectively.
| Lifestyle Changes for Heart and Oral Health | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Quit smoking | Reduces the risk of heart disease, gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancer |
| Adopt a heart-healthy diet | Supports cardiovascular health and prevents tooth decay and gum disease |
| Manage stress | Reduces the risk of heart problems and dental issues caused by stress-related habits |
By implementing these lifestyle changes, individuals can take proactive steps towards improving their heart and oral health. The benefits extend beyond these systems, contributing to overall well-being and a better quality of life.
Also Read – Swollen Gums Home Remedy: Quick Relief Tips
The Importance of Collaboration Between Dentists and Cardiologists
In the prevention of heart disease, collaboration between dentists and cardiologists plays a crucial role. By working together, these medical professionals can address both the oral health and cardiovascular health aspects, leading to better overall outcomes for patients.
Studies have shown a strong connection between oral health and heart disease. Poor oral health conditions, such as gum disease, can contribute to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular problems. This highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach that combines dental care and cardiac care to prevent heart disease.
Dentists have a unique opportunity to detect early signs of oral health conditions that may indicate an increased risk of heart disease. Through regular check-ups and examinations, dentists can identify issues such as gum disease, oral infections, and periodontal disease, which can potentially impact cardiovascular health.
Cardiologists, on the other hand, can help dentists by providing valuable insights into a patient’s cardiovascular health. Factors such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and any existing heart conditions can influence the approach to dental care and treatment planning.
By working collaboratively, dentists and cardiologists can develop personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs and medical history. This comprehensive approach ensures that both the oral health and cardiovascular aspects are taken into consideration, improving overall patient outcomes and reducing the risk of heart disease.
“Collaboration between dentists and cardiologists allows for a more holistic approach to healthcare, addressing both oral health and heart disease prevention. By combining their expertise, these professionals can provide patients with comprehensive care to protect both their smiles and their hearts.”
Benefits of Collaboration Between Dentists and Cardiologists:
- Early detection of oral health conditions that may indicate an increased risk of heart disease.
- Insights from cardiologists regarding cardiovascular health to inform dental treatment planning.
- Personalized treatment plans that address both oral health and cardiovascular health.
- Improved patient outcomes and reduced risk of heart disease through collaborative care.
Dental and Cardiac Conditions Benefitting from Collaboration:
| Dental Conditions | Cardiac Conditions |
|---|---|
| Gum disease | Coronary artery disease |
| Oral infections | Heart attack (myocardial infarction) |
| Periodontal disease | Stroke |
| Endocarditis (infection of the heart’s inner lining) | Heart failure |
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to understand the strong connection between oral health conditions and heart disease. Research has shown that maintaining good dental care and proper oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems. By prioritizing regular dental check-ups, proper brushing and flossing techniques, individuals can protect their heart health.
Collaboration between dentists and cardiologists is also paramount. A comprehensive approach that addresses both oral health and cardiovascular health can lead to better outcomes in preventing heart disease. Dentists and cardiologists should work together to develop tailored prevention strategies for individuals at risk, ensuring a holistic approach to overall health.
By acknowledging and acting upon this vital connection, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart health. Good oral hygiene practices and collaboration between dental and cardiac professionals can pave the way to a healthier future, reducing the burden of heart disease in our communities.
FAQ
What are some oral health conditions linked to heart disease?
Some oral health conditions linked to heart disease include gum disease (periodontal disease), dental infections, and oral inflammation.
How does dental health impact heart health?
Poor dental health, such as gum disease, can contribute to heart problems by allowing bacteria to enter the bloodstream and increase inflammation throughout the body.
What is the connection between oral bacteria and cardiovascular health?
Oral bacteria can travel from the mouth to the heart, causing infections in the heart valves or contributing to the formation of arterial plaque, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
What dental care practices can help prevent heart disease?
Maintaining good oral hygiene through regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings can contribute to heart disease prevention by reducing the build-up of plaque and the risk of oral infections.
How does gum disease affect heart health?
Gum disease increases the risk of heart disease by triggering chronic inflammation throughout the body, which can lead to the development of arterial plaque and contribute to cardiovascular problems.
What is the relationship between oral health and various heart conditions?
Oral health, especially the presence of oral bacteria and inflammation, has been linked to several heart conditions, including heart attack, stroke, and endocarditis.
What lifestyle changes can benefit both heart and oral health?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes quitting smoking, eating a balanced diet, managing stress, and exercising regularly can positively impact heart health and oral health.
Why is collaboration between dentists and cardiologists important for heart disease prevention?
Collaboration between dentists and cardiologists allows for a holistic approach to prevention by addressing both oral health and cardiovascular health, leading to better overall patient outcomes.